frame
view在父view坐标系统中的位置和大小。
bounds
view在本地坐标系中的位置和大小。
本地坐标系
每个view都有一个本地坐标系,这个坐标系的作用非常重要,比如触摸回调函数中的UITouch里面的坐标值就是参照这个本地坐标系的;当然bounds这个属性也是参照这个本地坐标系统来的。
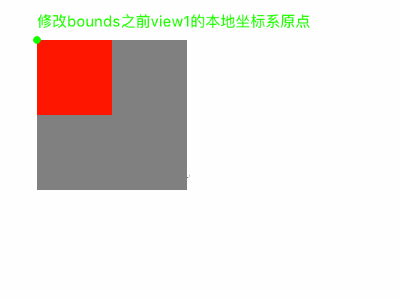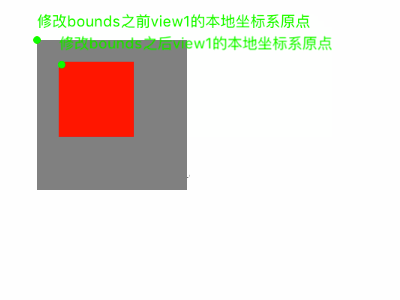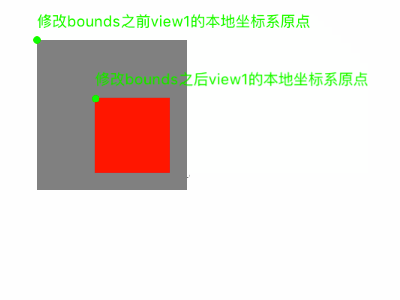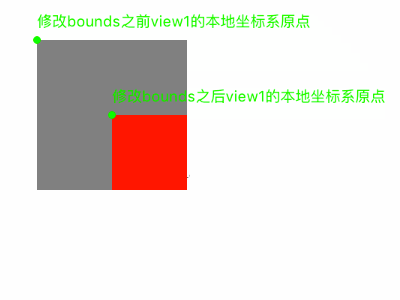
默认情况下,bounds的origin.x和origin.y为(0,0);也就是说,本地坐标系默认为原点为view的左上角位置。
我们可以修改bounds来改变本地坐标系。比如我们设置view的bounds的origin.x和origin.y为(-30,-30);那么,view左上角的位置坐标相对本地坐标系统为(-30,-30),那么本地坐标系的原点则在距离view右下角。
修改了自己的本地坐标系,本身的位置不会发生变化,而是影响其子视图的显示位置。
比如:
//view1
UIView *view1 = [[UIView alloc]initWithFrame:CGRectMake(50, 50, 100, 100)];
view1.backgroundColor = [UIColor grayColor];
[self.view addSubview:view1];
//view2
UIView *view2 = [[UIView alloc]initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 0, 50, 50)];
view2.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
[view1 addSubview:view2];
//修改view1的bounds,从而修改view1的本地坐标系,进而影响子视图的位置
[UIView animateWithDuration:2 animations:^{
[view1 setBounds:CGRectMake(-50, -50, 100, 100)];
}];
[view1 setBounds:CGRectMake(-50, -50, 100, 100)]这一行代码,我们修改了修改view1的bounds,从而修改view1的本地坐标系,进而影响子视图的位置。
产生的效果如下: